

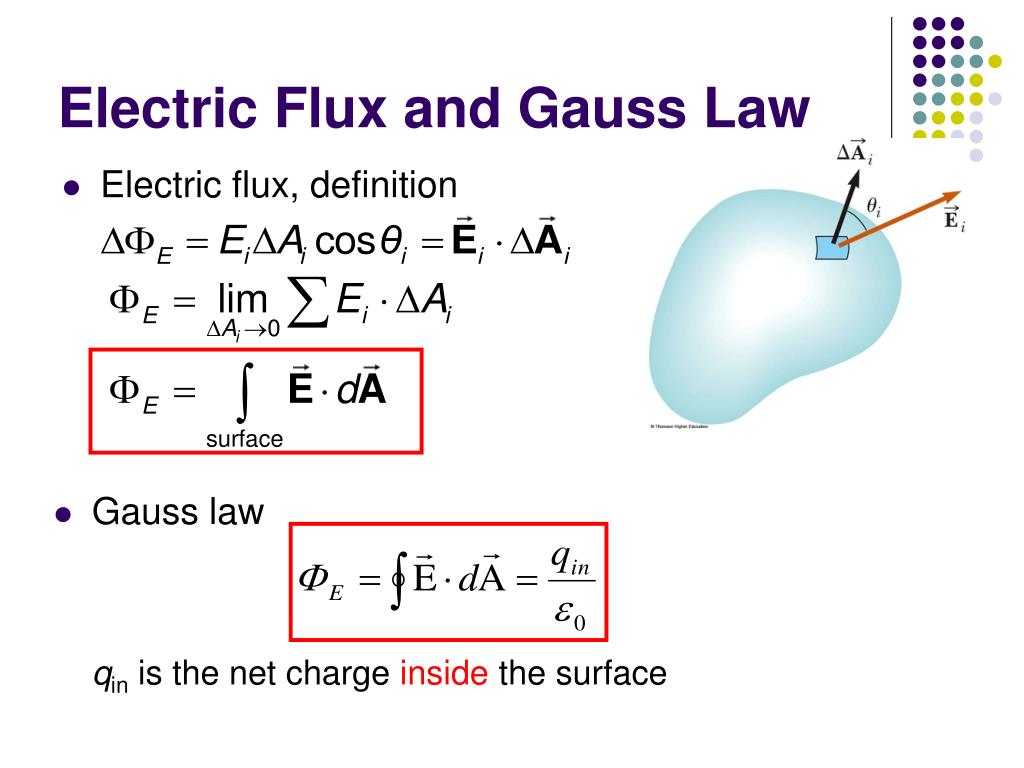
For example, the vector area of a rectangle of side lengths a = 5 cm and b = 4 cm has a magnitude of A = 5 cm × 4 cm = 20 cm 2 (20 units) and it is perpendicular to the plane of rectangle, as shown in the figure. Thus, instead of writing the surface area as A square units, we consider the corresponding area vector of A ⃗ units which is perpendicular to the given surface. This trick is especially common in electromagnetism. In some cases, it is convenient to appoint a vector to a given area, in order to make it operable with other vector quantities. For example, the area of a square of side length L is L × L = L 2, the area of rectangle of sides a and b is a × b, the area of a circle of radius R is π × R 2 and so on. Area is measured in square metres ( m 2). It is known from geometry that area is a scalar quantity, which represents the amount of surface enclosed within the boundary lines of a figure. But first, we have to explain what is electric flux and how can we find it. The concept of "electric flux" is very important in understanding the behaviour of electric current, for which we will discuss in the next chapter. What do you understand with the term "flux"? For example, what conclusion do you draw if somebody says, "the flux of people in the airport is large"? How does electric flux depend on the incidence angle of the field lines?ĭo you think the electric field depends on the number of lines crossing the surface of a charged plate?.
#Electric flux equation how to#
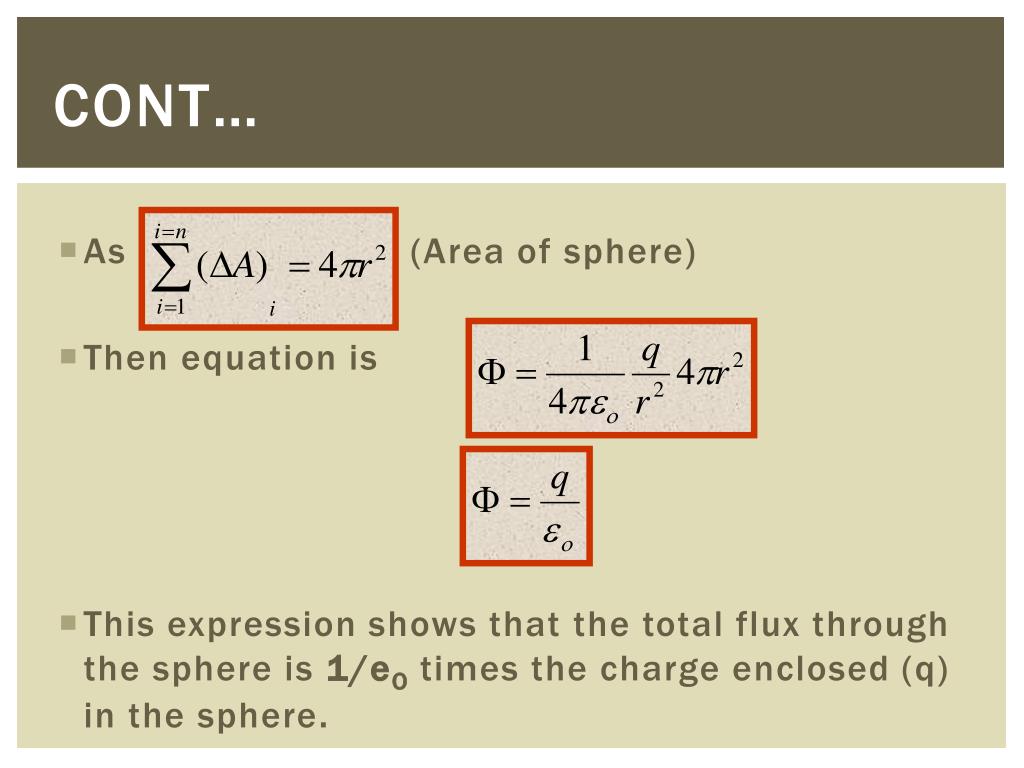
How to find the electric flux in some regular surfaces?.What is the electric flux of a point charge placed at centre of a sphere?.What is electric flux and how can we calculate it?.In this Physics tutorial, you will learn: Electrostatics Learning Material Tutorial ID


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
